Using OpenDNS is achieved by making a configuration change in the DNS settings of a network router, on individual computers, WiFi devices, or on internal DNS servers. Once OpenDNS is configured, administrators set and manage OpenDNS's advanced features, such as Web content filtering and security, by logging in to their OpenDNS account.
It is important to understand that OpenDNS advanced settings are applied to a network and those settings are subsequently inherited by all of the computers and devices that connect to that network.
Configuring OpenDNS means that OpenDNS is being specified as the DNS server for a network, usually in place of the DNS servers provided by an ISP. As the DNS server for a network, OpenDNS receives and answers the Internet DNS requests that originate from the computers and devices connected to that network.
For Enterprise networks, configuring OpenDNS typically means using OpenDNS as the forwarders of the organization's internal DNS servers. Since internal DNS server configurations can vary between a single server to multiple servers spread across departments and office locations, specific configurations will vary.
Ultimately, configuring OpenDNS is accomplished by changing a setting within a router, computer, device, or server; regardless of whether in a home, small business or Enterprise environment.
How to create a OpenDNS Account
Using bellow mentioned URL can make a free OpenDNS account for you
https://store.opendns.com/get/home-free?
then register with your E-mail id in the registration box and enter details of the same, after enter the details "click" continue ,then u will get a new window, see bellow image
Here u can see three sub divisions 1, computer. 2, Router. 3, DNS server. Then u can choose which type of configurations u want, and click the link
if you select computer, next you must enter which operating systems are using for installing openDNS,
if you select DNS server, you must enter which operating systems are using for installing openDNS,
if u select Router, u enter which type router you are using,
now we are selecting Router, that time u will get anew window like this.
Next click on which branded router using you are. I selected the NETGEAR router, then u will get a new window and follow this.
Change your settings: Configuration for NETGEAR
1. Type the router's setup URL (http://192.168.0.1) into a web browser address bar
http://192.168.0.1 is the default Netgear router IP address.
(http://192.168.1.1 will work for some Netgear models.)
2. Enter the password.
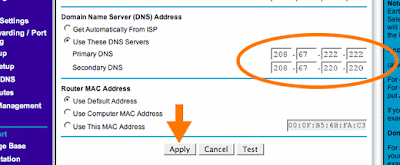
3. Type in OpenDNS addresses in Primary DNS and Secondary DNS fields.
Please write down your current DNS settings before switching to OpenDNS, in case you want to return to your old settings for any reason.
The addresses for OpenDNS are:
208.67.222.222
208.67.220.220
Note: The Netgear WGR614 versions require a firmware upgrade in order to be compatible with OpenDNS. Click here to upgrade
4. Click Apply button.
5. Wait for the settings to be updated.
6. Open Dashboard
Next you will get a new window like this
Type Your own WAN IP in red marked box and Click "add this network". then you will get a new settings window like this.
You can select the WAN IP in the red marked section from this window, after selecting the IP you will get a new window as follows,
In this section, you can select which type of filtering you want(High, Moderate, Low, None or Custom)
In the High filtering you want block bellow site categories
Adware
- Sites that distribute applications which display advertisements without user's knowledge or choice. Does NOT include sites which serve advertising.
- Alcohol
Sites about alcohol use, commercial and otherwise.
- Chat
Sites where you can chat in real-time with groups of people. Includes IRC and video chat sites.
- Classifieds
Sites for buying and selling (or bartering) goods and services. Includes sites with real estate and housing listings.
- Dating
Sites for meeting other people.
- Drugs
Sites about illegal or recreational drug use.
- File storage
Sites that offer space for hosting, sharing and backup of digital files.
- Gambling
Sites that offer gambling or information about gambling.
- Games
Sites that offer game play and information about games (news, tips, cheat codes).
- Hate/Discrimination
Sites that promote intolerance based on gender, age, race, nationality, religion, sexual orientation or other group identities.
- Instant messaging
Sites that offer access or software to communicate in real-time with other individuals.
- P2P/File sharing
Sites that facilitate the sharing of digital files between individuals, especially via peer-to-peer software, including torrent sites.
- Social networking
Sites that promote interaction and networking between people.
- Video sharing
Sites for sharing video content.
- Visual search engines
Sites for searching for images based on keywords.
- Weapons
Sites about weapons, commercial and otherwise.
- Webmail
Sites that offer the ability to send or receive email.
- Photo sharing
Sites for sharing photographs, as individual images, galleries and albums.
- Adult Themes
Sites that are adult in nature and are not defined in other rating categories. Note: This category should only be turned on if you want to be very restrictive on your network.
- Tasteless
Sites that contain information on such subjects as mutilation, torture, horror, or the grotesque.
- Lingerie/Bikini
Sites displaying or dedicated to lingerie/bikini that could be considered adult-only.
- Proxy/Anonymizer
Sites providing proxy bypass information or services. Also, sites that allow the user to surf the net anonymously, including sites that allow the user to send anonymous emails.
- Sexuality
Sites that provide information, images or implications of bondage, sadism, masochism, fetish, beating, body piercing or self-mutilation.
- Nudity
Sites that provide images or representations of nudity.
- Pornography
Anything relating to pornography, including mild depiction, soft pornography or hard-core pornography.
- Forums/Message boards
Sites with discussions, including bulletin boards, message boards and forums.
In the Moderate filtering you want block bellow site categories
- Adware
Sites that distribute applications which display advertisements without user's knowledge or choice. Does NOT include sites which serve advertising.
- Alcohol
Sites about alcohol use, commercial and otherwise.
- Dating
Sites for meeting other people.
- Drugs
Sites about illegal or recreational drug use.
- Gambling
Sites that offer gambling or information about gambling.
- Hate/Discrimination
Sites that promote intolerance based on gender, age, race, nationality, religion, sexual orientation or other group identities.
- Weapons
Sites about weapons, commercial and otherwise.
- Tasteless
Sites that contain information on such subjects as mutilation, torture, horror, or the grotesque.
- Lingerie/Bikini
Sites displaying or dedicated to lingerie/bikini that could be considered adult-only.
- Proxy/Anonymizer
Sites providing proxy bypass information or services. Also, sites that allow the user to surf the net anonymously, including sites that allow the user to send anonymous emails.
- Sexuality
Sites that provide information, images or implications of bondage, sadism, masochism, fetish, beating, body piercing or self-mutilation.
- Nudity
Sites that provide images or representations of nudity.
- Pornography
Anything relating to pornography, including mild depiction, soft pornography or hard-core pornography.
In the Low filtering you want block bellow site categories
- Tasteless
Sites that contain information on such subjects as mutilation, torture, horror, or the grotesque.
- Proxy/Anonymizer
Sites providing proxy bypass information or services. Also, sites that allow the user to surf the net anonymously, including sites that allow the user to send anonymous emails.
- Sexuality
Sites that provide information, images or implications of bondage, sadism, masochism, fetish, beating, body piercing or self-mutilation.
- Pornography
Anything relating to pornography, including mild depiction, soft pornography or hard-core pornography.
In the None filtering you cannot block any sites categories
In the Custom filtering you want block any site categories with your choice.
Next we selected "Custom" filtering mode, then u can get a sub menu like this
You can choose different site categories from here for blocking your network, then Click Apply, now u are successfully created OpenDNS in your Network,
After completing the OpenDNS configuration you must change all computer Preferred DNS and Alternate DNS
Preferred DNS 208.67.222.222
Alternate DNS 208.67.220.220